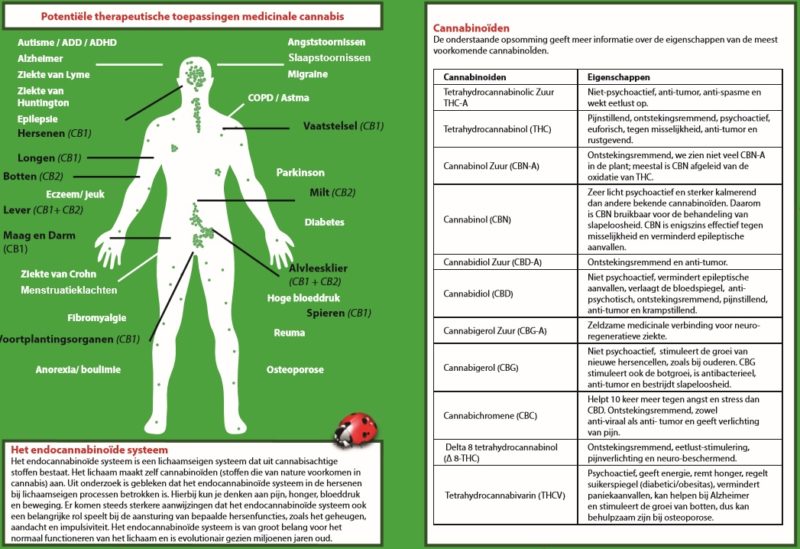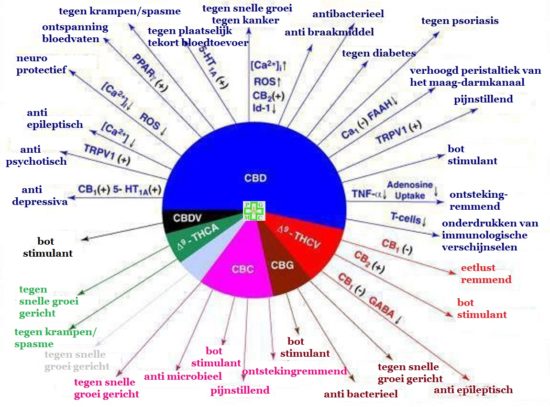
Cannabis is a plant that has been used for medicinal purposes for centuries. In recent years, cannabinoids, the active compounds in cannabis, have been researched extensively for their potential therapeutic benefits. These compounds have been found to interact with the human body’s endocannabinoid system, which regulates a variety of physiological processes. In this article, we will explore the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids in the treatment of various conditions.
What are Cannabinoids?
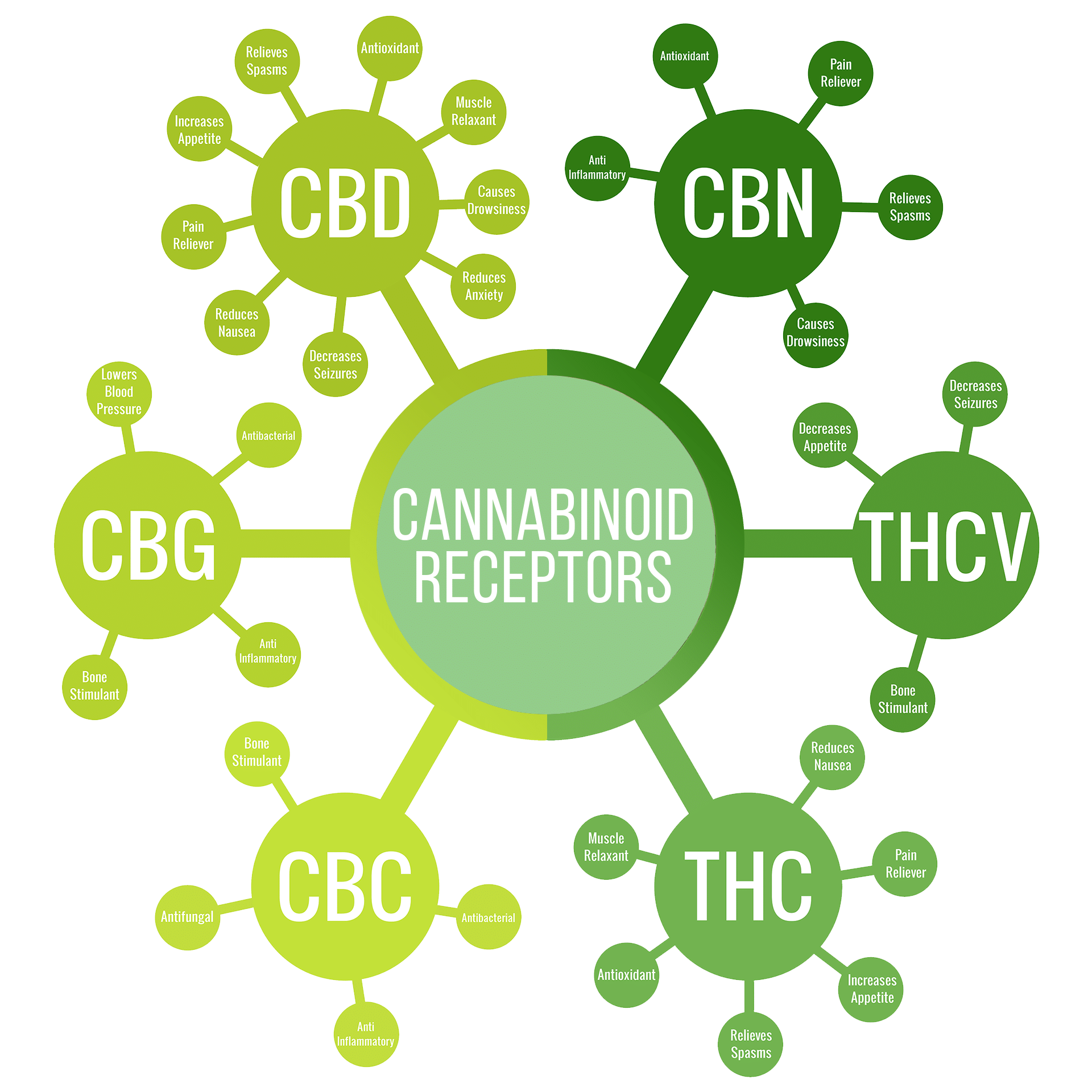
Cannabinoids are a group of chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant. The two most well-known cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). THC is responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis, while CBD is non-psychoactive. There are over 100 different cannabinoids in cannabis, each with its own potential therapeutic benefits.
The Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex system in the human body that regulates various physiological processes, including pain, mood, appetite, and immune function. The ECS consists of receptors, endocannabinoids (compounds produced by the body), and enzymes that break down endocannabinoids. Cannabinoids from the cannabis plant can interact with the ECS to produce therapeutic effects.
Cannabinoids and Pain Management
Cannabinoids have been found to be effective in managing pain, including chronic pain. THC has been shown to reduce pain by activating the ECS and decreasing inflammation. CBD has been found to reduce pain by blocking pain signaling and reducing inflammation. Cannabinoids may also be effective in reducing neuropathic pain.
Cannabinoids and Anxiety Disorders
Cannabinoids have shown promise in the treatment of anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). CBD has been found to reduce anxiety by increasing serotonin levels in the brain. THC may also have anti-anxiety effects, but its psychoactive effects may worsen anxiety in some individuals.
Cannabinoids and Epilepsy
Cannabinoids have been found to be effective in the treatment of epilepsy, particularly in children with treatment-resistant epilepsy. CBD has been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures in some individuals. The FDA has approved a CBD-based medication, Epidiolex, for the treatment of two rare forms of childhood epilepsy.
Cannabinoids and Cancer Treatment
Cannabinoids have shown promise in the treatment of cancer, particularly in reducing nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy. THC has been shown to be effective in reducing nausea and vomiting, while CBD may have anti-tumor effects. More research is needed to fully understand the potential of cannabinoids in cancer treatment.
Cannabinoids and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Cannabinoids have shown potential in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. CBD has been found to have neuroprotective effects, while THC may improve motor function and reduce tremors associated with Parkinson’s disease.
Cannabinoids and Inflammatory Conditions
Cannabinoids have been found to be effective in reducing inflammation associated with various conditions, such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and multiple sclerosis (MS). CBD has been shown to reduce inflammation by inhibiting inflammatory cytokines, while THC may reduce inflammation by activating the ECS.
Cannabinoids and Addiction
Cannabinoids have been studied for their potential in treating addiction to drugs, such as opioids and cocaine. CBD has been found to reduce drug-seeking behavior in animal studies, while THC may reduce withdrawal symptoms associated with opioid addiction. More research is needed to fully understand the potential of cannabinoids in addiction treatment.
Limitations and Future Directions
While cannabinoids show promise in the treatment of various conditions, there are limitations to their use. THC’s psychoactive effects may not be desirable for some individuals, and the long-term effects of cannabis use are not fully understood. More research is needed to fully understand the potential of cannabinoids in various conditions and to develop safe and effective cannabinoid-based treatments.
Conclusion: The Promising Future of Cannabinoids in Medicine
Cannabinoids have shown promise in the treatment of various conditions, including pain, anxiety disorders, epilepsy, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. CBD, in particular, has been found to have a variety of therapeutic benefits with few side effects. As research in this area continues, we may see more cannabinoid-based treatments becoming available for patients. However, it is important to continue to study the potential risks and limitations of cannabinoids to ensure their safe and effective use in medicine.
In conclusion, the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids are immense, with research continuing to show new findings. As we continue to study the potential of these compounds, we must remain mindful of the limitations and potential risks. With more research and development in the future, we may see more effective and safe cannabinoid-based treatments become available to patients.