Unlocking the Mysteries of Anandamide: Cannabis, Bliss, and Medical Potential
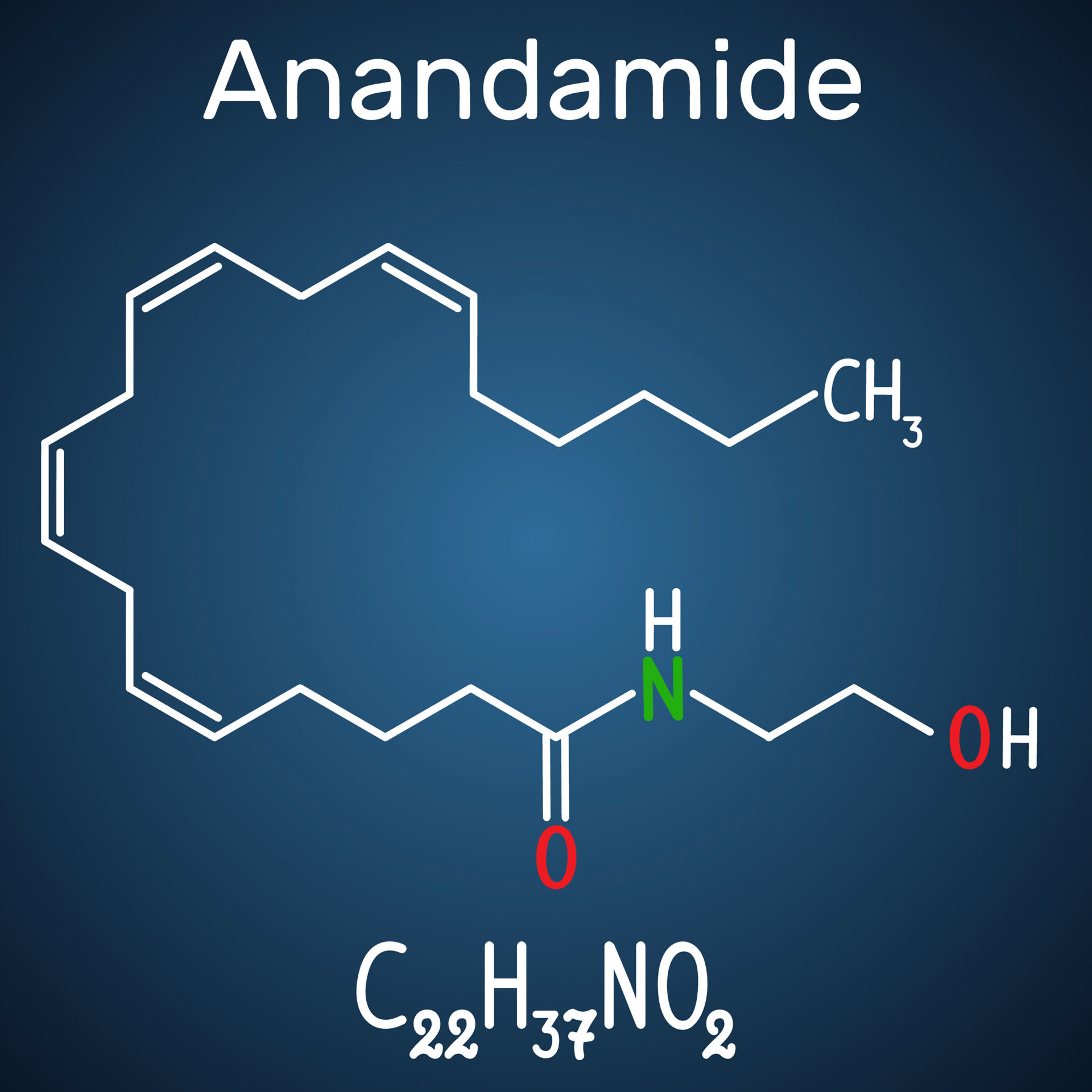
Anandamide is a fascinating molecule that has been gaining interest in the scientific community for its potential medical benefits. It is a neurotransmitter that belongs to a class of molecules called endocannabinoids, which interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, such as pain, appetite, and mood, among others. Understanding the science behind anandamide and its effects on the body and brain can provide insights into the therapeutic potential of cannabis and its derivatives.
Unveiling the Science of Anandamide
Anandamide was first discovered in the early 1990s by Israeli scientist Raphael Mechoulam and his team. They named it after the Sanskrit word “ananda,” which means “bliss,” due to its reported mood-enhancing effects. Anandamide is produced naturally in the body and is synthesized from arachidonic acid, which is found in various foods, including nuts, seeds, and meat. It is primarily synthesized in the brain and acts as a neurotransmitter, signaling molecules that transmit information between nerve cells.
Cannabis and the Endocannabinoid System
Cannabis is a plant that contains over 100 different cannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). These compounds interact with the ECS, which consists of two main types of receptors: CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and nervous system, while CB2 receptors are more prevalent in the immune system and peripheral tissues. THC binds to CB1 receptors and is responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis, while CBD has a more subtle impact on the ECS.
Anandamide: The “Bliss Molecule”
Anandamide is often referred to as the “bliss molecule” due to its reported euphoric effects. It is believed to play a role in reward and pleasure pathways in the brain and is released during activities such as exercise, sex, and meditation. Anandamide is also involved in the regulation of appetite and sleep, as well as the immune response and pain perception.
How Anandamide Affects the Body and Brain
Anandamide’s effects on the body and brain are complex and multi-faceted. It interacts with various neurotransmitter systems, including dopamine, serotonin, and GABA, among others. Anandamide is also involved in the regulation of inflammatory processes and has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, anandamide has been linked to neuroprotective effects and may play a role in the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Anandamide’s Role in Pain Management
Anandamide has been shown to have analgesic (pain-relieving) effects and is involved in the regulation of pain perception. It binds to CB1 receptors in the brain and spinal cord, which can reduce the transmission of pain signals. Anandamide also interacts with other pain-relieving systems in the body, such as the opioid system.
The Link Between Anandamide and Appetite
Anandamide is involved in the regulation of appetite and has been shown to stimulate the release of hormones that increase hunger. This effect is mediated through its interaction with CB1 receptors in the hypothalamus, which is a region of the brain that controls appetite and metabolism. However, chronic cannabis use has been associated with weight gain and obesity, which may be due to the overstimulation of the ECS.
Anandamide’s Potential for Mood Disorders
Anandamide’s role in mood regulation is complex and not fully understood. It has been shown to have anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effects and may play a role in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Anandamide is also involved in the regulation of depression-like behaviors in animal models, although its effects in humans are less clear. Some studies have suggested that low levels of anandamide may be associated with depression and that increasing anandamide levels may have antidepressant effects.
Anandamide and Neuroprotection
Anandamide has been shown to have neuroprotective effects and may play a role in the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases. It has been shown to reduce brain damage in animal models of stroke and traumatic brain injury. Anandamide’s neuroprotective effects are thought to be mediated through its interaction with CB1 receptors and its anti-inflammatory properties.
Anandamide’s Cardiovascular Benefits
Anandamide has been shown to have cardiovascular benefits, particularly in the regulation of blood pressure. It acts as a vasodilator, which means it can widen blood vessels and improve blood flow. Anandamide has also been shown to reduce inflammation in blood vessels and may play a role in the prevention of atherosclerosis.
Anandamide and Reproductive Health
Anandamide plays a role in reproductive health and has been shown to affect fertility in both men and women. It is involved in the regulation of ovulation and the menstrual cycle in women and has been linked to sperm motility and function in men. Anandamide also plays a role in the development of the placenta during pregnancy.
How Cannabinoids Affect Anandamide Levels
Cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, can affect anandamide levels in the body. THC binds to CB1 receptors and can increase anandamide levels, while CBD has been shown to inhibit the breakdown of anandamide, leading to increased levels. The balance between THC and CBD in cannabis products can influence the overall effect on anandamide levels and ECS function.
Medical Potential of Anandamide and Its Derivatives
Anandamide and its derivatives have potential medical applications in a variety of conditions, including pain management, mood disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Researchers are exploring the use of anandamide analogs, which are synthetic compounds that mimic the effects of anandamide, for therapeutic purposes. Additionally, cannabis-derived products, such as CBD oil, have gained popularity as alternative treatments for various health conditions.
Unlocking the Mysteries of Anandamide: Cannabis, Bliss, and Medical Potential
Anandamide is a fascinating molecule with wide-ranging effects on the body and brain. Its role in the regulation of pain, appetite, and mood, among other processes, has led to increased interest in its potential medical applications. Understanding the science behind anandamide and its interaction with the ECS can provide insights into the therapeutic potential of cannabis and its derivatives. As research continues, we may uncover more mysteries of anandamide and its medical potential.